Analysis of relationship between extrusion speed of Aluminum Porcelain Tile Trim Profiles and various factors
It also introduces several new extrusion processes and product defects, and puts forward specific measures for choosing the extrusion speed correctly. Key words: extrusion speed; influencing factors; product defect; solution
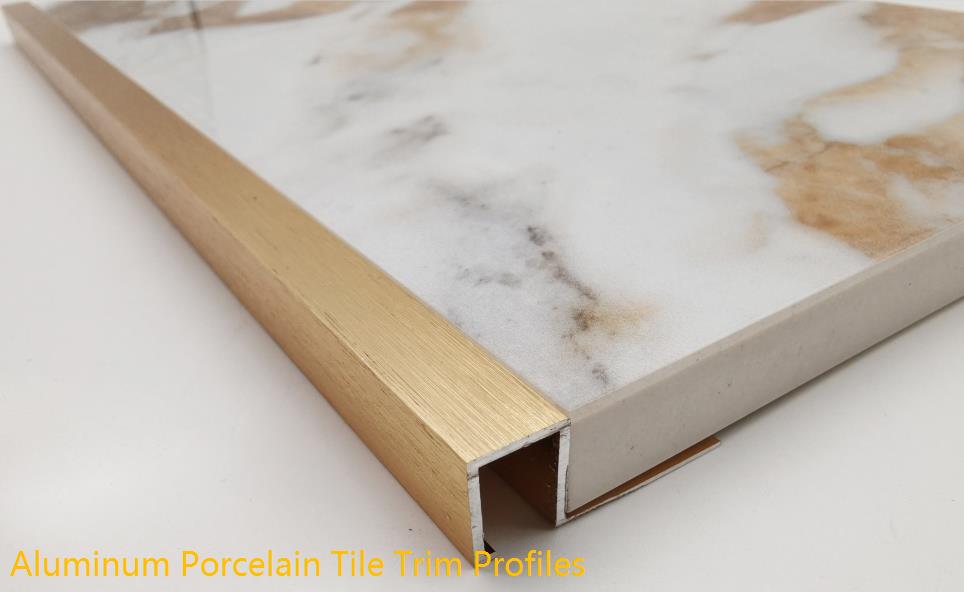

The extrusion speed refers to the flow rate of the product or the speed at which the main plug of the extruder moves forward. In actual production, the flow rate of products is controlled by adjusting the forward speed of the main plunger of the extruder. Extrusion speed is an important factor that affects production efficiency, and also affects product quality (such as product surface and size, etc.), so the appropriate extrusion speed is very important. The extrusion speed of 6063 aluminum alloy profile (die exit speed) ranges from 9 to 60 m/min, among which the solid part is 9 to 20 m/min.
The size of the extrusion speed is related to factors such as alloy type, ingot state and size, product shape, degree of deformation (or extrusion coefficient), deformation temperature, tool (die) structure and process conditions.
1.1 The influence of the quality of the ingot The quality index of the ingot is mainly the grain size of the first grade, the hydrogen content is less (0.1mL/100g aluminum), the slag is small and fine (the slag grains above 0.008 mm are removed), and the metallographic structure is uniform. Cracks, porosity, pores and element segregation. In this way, the plasticity and deformability of the ingot are good, the extrusion force of the Aluminum Porcelain Tile Trim Profiles is reduced, and the extrusion speed is increased. Otherwise, the extrusion speed will be slow and the die will be worn out.
1.2 The influence of extrusion temperature When metal is extruded, as the temperature increases, the non-uniformity of metal fluidity will increase. During the entire extrusion process, the temperature of the ingot in the deformation zone gradually increases, and the faster the extrusion speed, the higher the temperature, and the temperature rise can reach about 100C. When the metal temperature in the deformation zone exceeds the maximum allowable critical deformation temperature, the metal will enter a hot brittle state and form extrusion cracks. Therefore, when the ingot temperature is high, the extrusion speed must be gradually reduced during the extrusion process. The 6063 aluminum alloy ingot is generally preheated to 480~520C, and the extrusion barrel is preheated to 400~450.
1.3 The influence of Aluminum Porcelain Tile Trim Profiles dimensions and shape The Aluminum Porcelain Tile Trim Profiles dimensions and geometry have obvious influence on the metal outflow rate of extruded products. The general rule is: the geometric shape of the product is simple, the symmetry is good, and the product with a small width-to-thickness ratio can be relatively taller; on the contrary, the product with complex geometrical size, large width-to-thickness ratio, large wall thickness difference, and poor symmetry should be relatively slow. Some. Under the same conditions, the thinner the wall thickness of the product, the more uniform the deformation of the product along the cross-section, the smaller the tendency to produce extrusion cracks. Therefore, the extrusion speed can be faster.
1.4 The degree of deformation affects the degree of deformation. The greater the degree of deformation of the product, the greater the required extrusion force, and the greater the heat of metal deformation, so the flow rate of the product is slower; on the contrary, the degree of deformation is small and the metal flows evenly, so the extrusion speed It can be faster. 1.5 The influence of mold structure When aluminum alloy profile is extruded, the type of mold core used is determined by the characteristics of the profile. Generally, solid profiles use plane molds, and hollow profiles use tongue-shaped or split-flow combined molds. For 6063 alloy, flat die has lower resistance than tongue die or split-flow combined die, so the extrusion speed can be higher. For the mold core with the same structure, the wider the working belt of the mold core, the greater the friction between the alloy and the working belt, the greater the additional tensile stress on the surface of the product, and the higher the tendency for extrusion cracks on the surface of the product. Therefore, the extrusion speed needs to be reduced accordingly. Secondly, from the perspective of the friction between the metal and the core working belt, the harder and smoother the core working belt, the faster the extrusion speed.

With the development of modern technology, new processes have emerged to increase the pressing speed, and new extrusion processes such as isothermal extrusion, isostatic extrusion, constant velocity extrusion, high temperature extrusion, low temperature extrusion and nitrogen cold extrusion have been developed.
2.1 Isothermal extrusion process Isothermal extrusion is to keep the temperature in the deformation zone within a constant range by automatically adjusting the extrusion speed to achieve the purpose of rapid extrusion. In particular, some equipment is equipped with a microcomputer device. To achieve the purpose of automatically controlling the extrusion speed.
2.2 Low temperature rapid extrusion process The low temperature rapid extrusion temperature adopts 440~460℃. This technology was applied earlier in Japan's Beixing Aluminum Company. They extruded 6063 aluminum alloy at 430℃, the extrusion speed is 30-50 m/min, the upper limit is taken for the flat die, and the lower limit is taken for the hollow die. my country's Fujian Nanping Aluminum Plant is a domestically mature unit that adopts this technology. Low temperature technology refers to the temperature of entering the mold, and the temperature of exiting the mold must reach the best temperature range of air-cooling quenching (515~525℃), otherwise the hardness and strength of the profile will be unqualified. How to achieve the desired mold temperature during extrusion is the key to applying this technology.
2.3 The high-temperature slow-speed extrusion process has a high-temperature slow-speed extrusion temperature of 500~520℃, which must not be fast during extrusion.
This is because: First, the mold temperature is higher than 525℃, and when the air cooling is insufficient, the product often produces a large and coarse grain structure; the second magnesium and silicon cannot be completely dissolved, and the alloy hardness and strength are low; its three-way combination Die, such as extrusion too fast, high temperature, insufficient metal supply, forming a loose structure along the shunt line, easy to be corroded and exposed during alkaline washing, which affects the quality of post-processed profiles. So the squeeze speed should be slower-better.
2.4 Nitrogen cold extrusion process leads the cold liquid nitrogen stored in the tank to the working belt of the extrusion die during the extrusion process. One can reduce the contact friction between the product and the core working belt; the second can cool the extrusion die and the deformation zone to take away the deformation heat, and at the same time, the outlet of the core is controlled by nitrogen, which not only reduces the oxidation of the product surface, It also reduces the adhesion and accumulation of alumina. Therefore, nitrogen cold extrusion not only improves the surface quality of the product, but also greatly increases the extrusion speed.
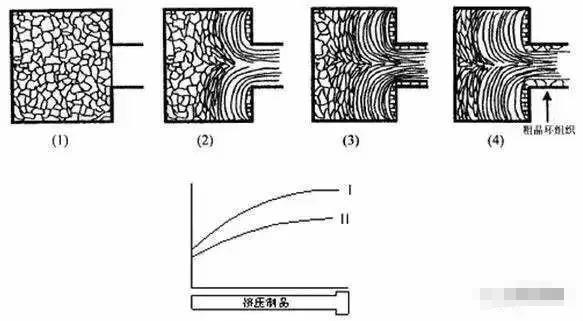
In the extrusion production of Aluminum Porcelain Tile Trim Profiles, the common stocks and causes due to improper extrusion speed are shown in Table 1.
Cause | Waste phenomeno |
The extrusion outflow speed is too fast and the deformation speed is too fast, the deformation tensile stress exceeds the tensile strength, which destroys the continuity of the tissue and produces cracks, which often appear at the tail and edge of the product | crack |
Extrusion temperature is too high, speed is too fast | Needle-shaped white stripes with tails appear on the surface |
If the extrusion speed is too fast, the heat of metal deformation is large, and the metal is easy to bond to the working belt of the core, which will cause pitting of the product | Pockmarked |
Improper speed control, uneven flow velocity along the entire extrusion die section, waves on one side too fast | wave |
For hollow profiles with a large inner cavity or profiles with a large width-to-thickness ratio, if the front end of the product flows out too fast, the hollow profile will flaring; if the front end of the product flows out slowly, the hollow material will shrink. | Variations in Profile Dimensions |
The extrusion speed is fast, and the tendency of metal to flow unevenly along the extrusion direction increases. At the end of extrusion, the dirt on the surface of the ingot enters the interior of the product, forming a shrinkage | Profile shrinking |
This is a block of text. Double-click this text to edit it.
Table 1 Effect of extrusion speed on product quality Causes of waste phenomenon Cracks Extrusion outflow speed and deformation speed are too fast, the deformation tensile stress exceeds the tensile strength, the continuity of the organization is destroyed and cracks occur, often appearing in Needle-like extrusion appears on the surface of the tail and edge of the product. The temperature is too high and the speed is too fast. The extrusion speed is too fast, and the heat of metal deformation is large. Improper speed control, uneven flow velocity along the entire section of the extrusion die, too fast--the side produces waves. For hollow profiles with large inner cavity or profiles with large width-thickness ratio, the front end of the product flows out too fast, resulting in hollow profiles. Flaring; if the outflow speed of the front end of the product is slow, the extrusion speed of the hollow material will be fast, and the uneven flow tendency of the metal along the extrusion direction will increase. At the end of extrusion, dirt on the surface of the ingot will enter the interior of the product. Form indentation.
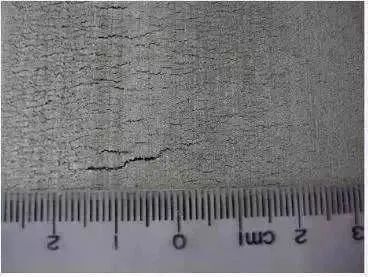
( 1 ) To improve the quality of aluminum alloy ingots, adopt suitable extrusion process parameters and high-quality molds to improve product quality and efficiency.
(2) During production, the operator should properly control and adjust the extrusion speed according to the shape, size, degree of deformation, mold structure and process parameters of the product, so as to improve product quality.
(3) Actively research new extrusion technology to improve product quality and production efficiency.
 For More Information
For More Information